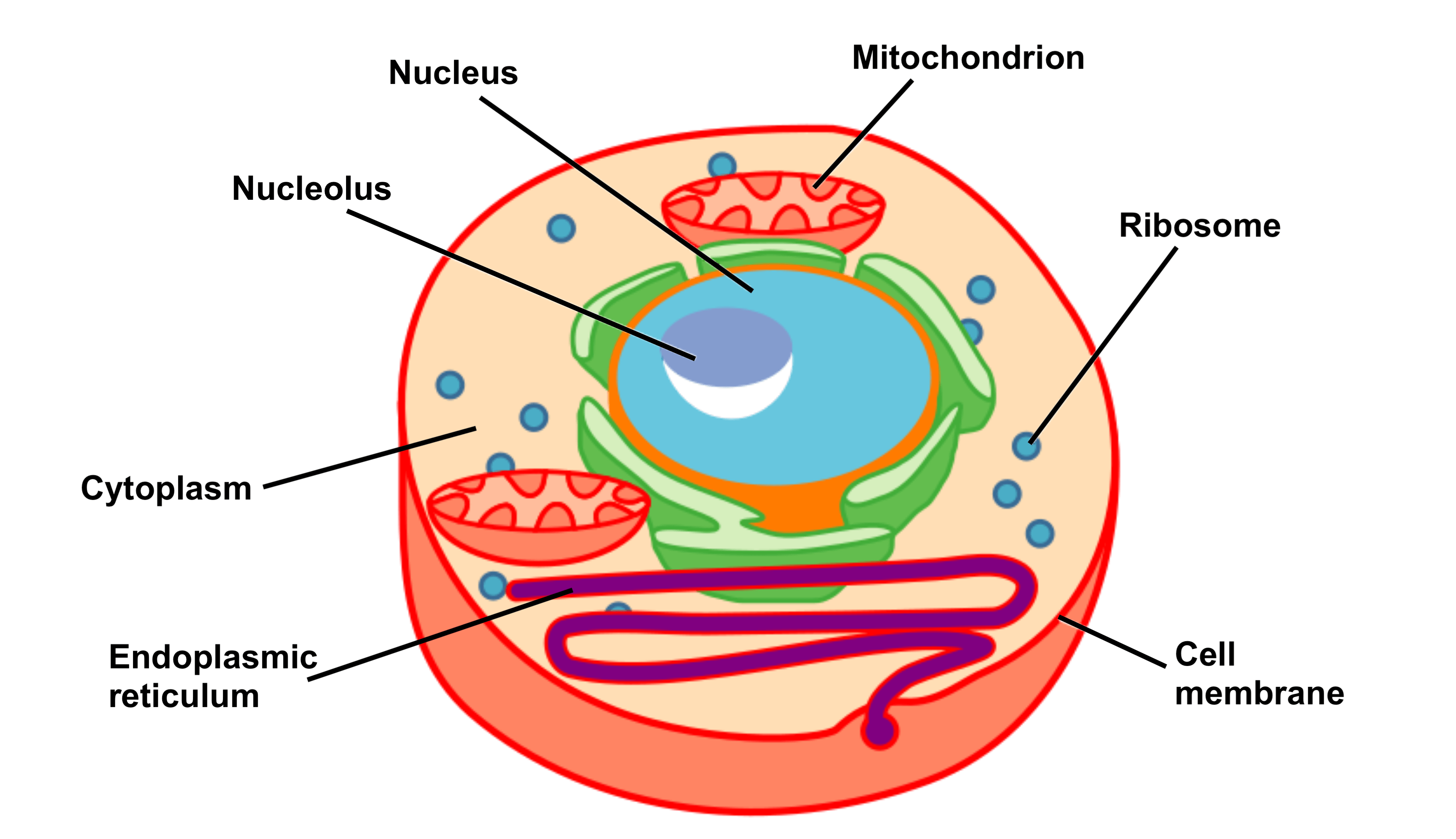
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 The Organelles Medical Exam Prep
Animal Cell: Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram. June 6, 2023 by Faith Mokobi. Edited By: Sagar Aryal. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall.

Eukaryotic cell structure diagrams Biological Science Picture Directory
Nucleus. The nucleus of a cell contains chromatin (a complex of DNA and histone proteins) which is the genetic material of the cell . Present in all eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is relatively large and separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane (the nuclear envelope) which has many pores; Nuclear pores are important channels for allowing mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus.

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
Parts, Functions & Diagrams. Although there are differences among eukaryotes (creature that range from amoebae to elephant), overall, eukaryotic cells share many characteristics. Here's a breakdown. Article Summary: Animals, plants, fungi, protists, algae, and water & slime molds are eukaryotes, organisms composed of one or more nucleated cells.
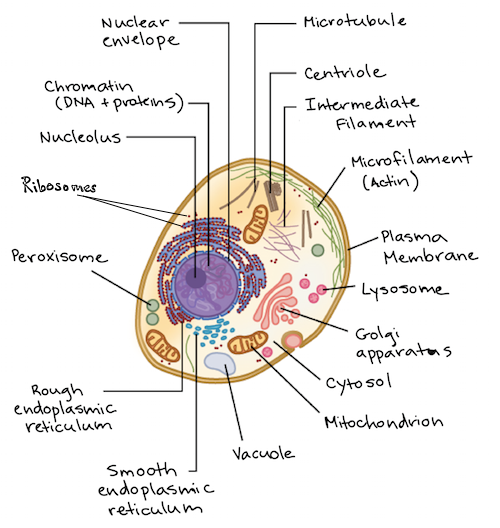
31 Identify And Label Each Part Of This Eukaryotic Cell Labels For Your Ideas
. Cells of animals, plants and fungi are called eukaryotic cells . Comparing cell types A group of organisms called Archaea are also prokaryotic. Next page Plant and animal cells Previous.

Parts and functions of eukaryotic cell
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.

Eukaryotic Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Diagram Cell Cycle Examples What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
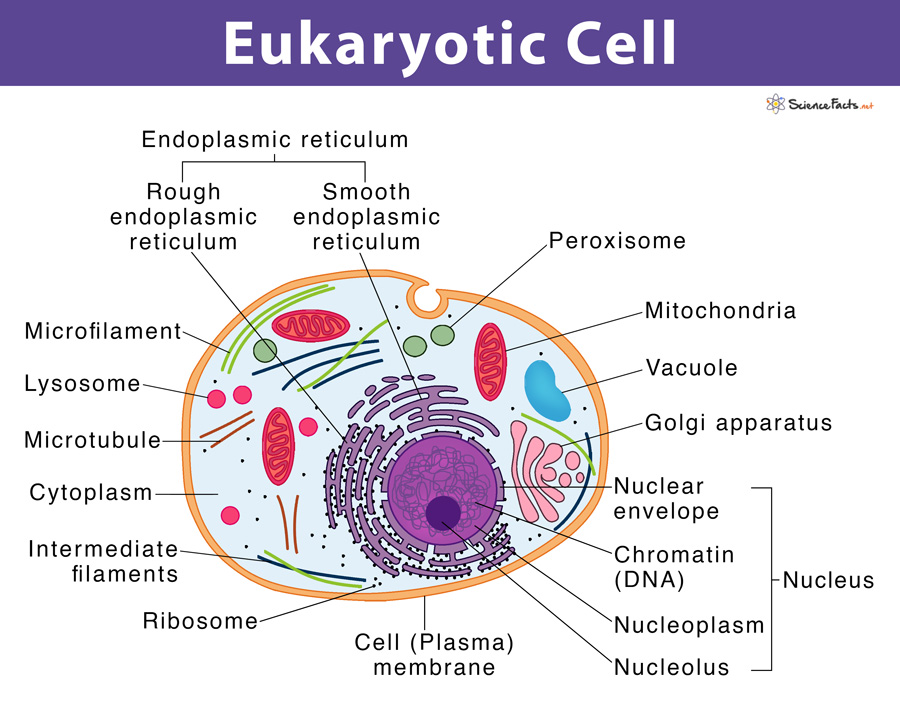
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples
4: Cell Structure 4.6: Eukaryotic Cells - Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Chloroplast Chloroplasts are found in the green parts of a plant - the green colour a result of the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll Larger than mitochondria, also surrounded by a double-membrane Membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids containing chlorophyll stack to form structures called grana

Eukaryotic Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
What exactly are eukaryotic cells? They're one of two major classifications of cells - eukaryotic and prokaryotic. They're also the more complex of the two. Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus.
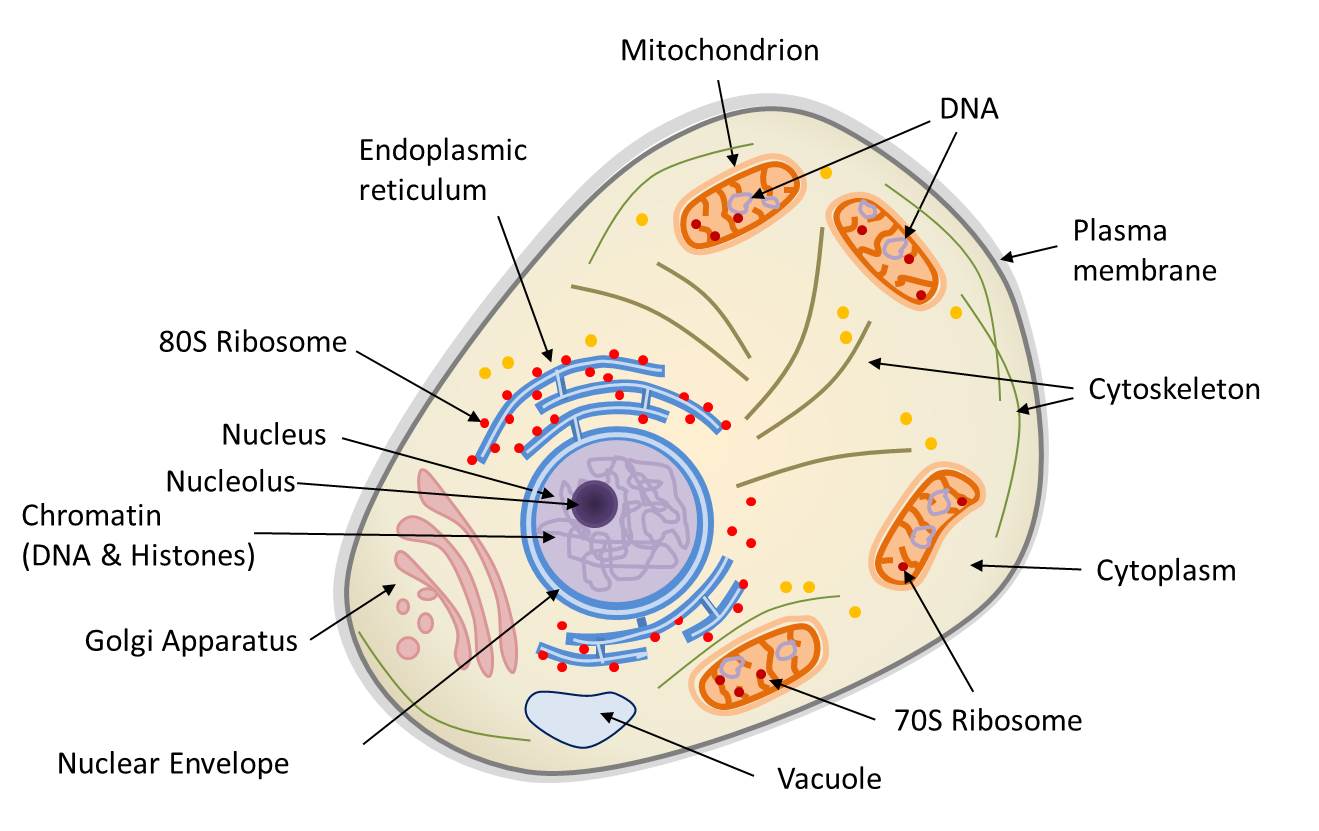
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell Encyclopedia of the Environment
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus.".

Eukaryotic Cell
What are the different types of eukaryotic cells? What are the double membrane bounded organelles in eukaryotic cells? What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?

1.4. Eucaryotic cell structure Biolulia European Sections
There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi.
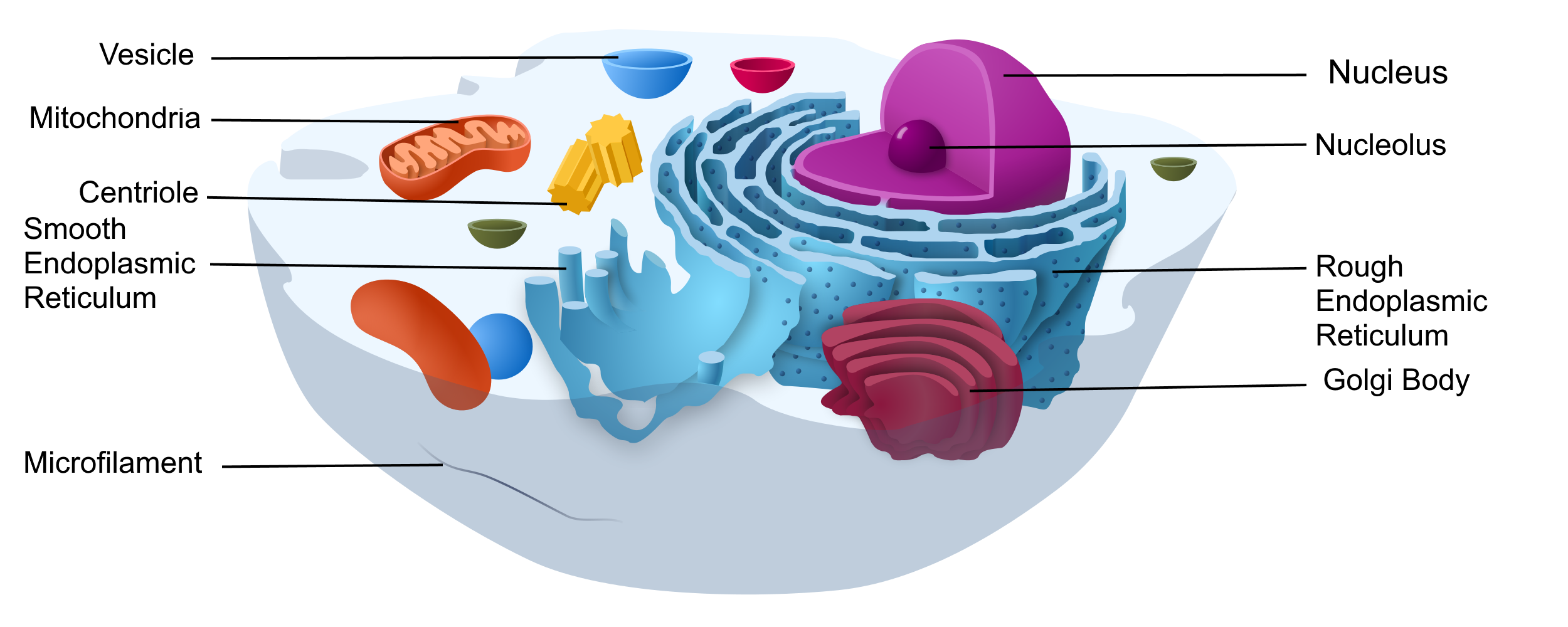
4.3 Variation in Cells Human Biology
Understanding: • Eukaryotes have a compartmentalised cell structure Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus ('eu' = good / true ; 'karyon' = nucleus) They have a more complex structure and are believed to have evolved from prokaryotic cells (via endosymbiosis)

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.

Figure 1.1. Eukaryotic Cell Numerous membranebound organelles are found in the cytoplasm of a
Figure 4.7.1 4.7. 1: Eukaryotic Plasma Membrane: The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids. Cholesterol, also present, contributes to the fluidity of the membrane.
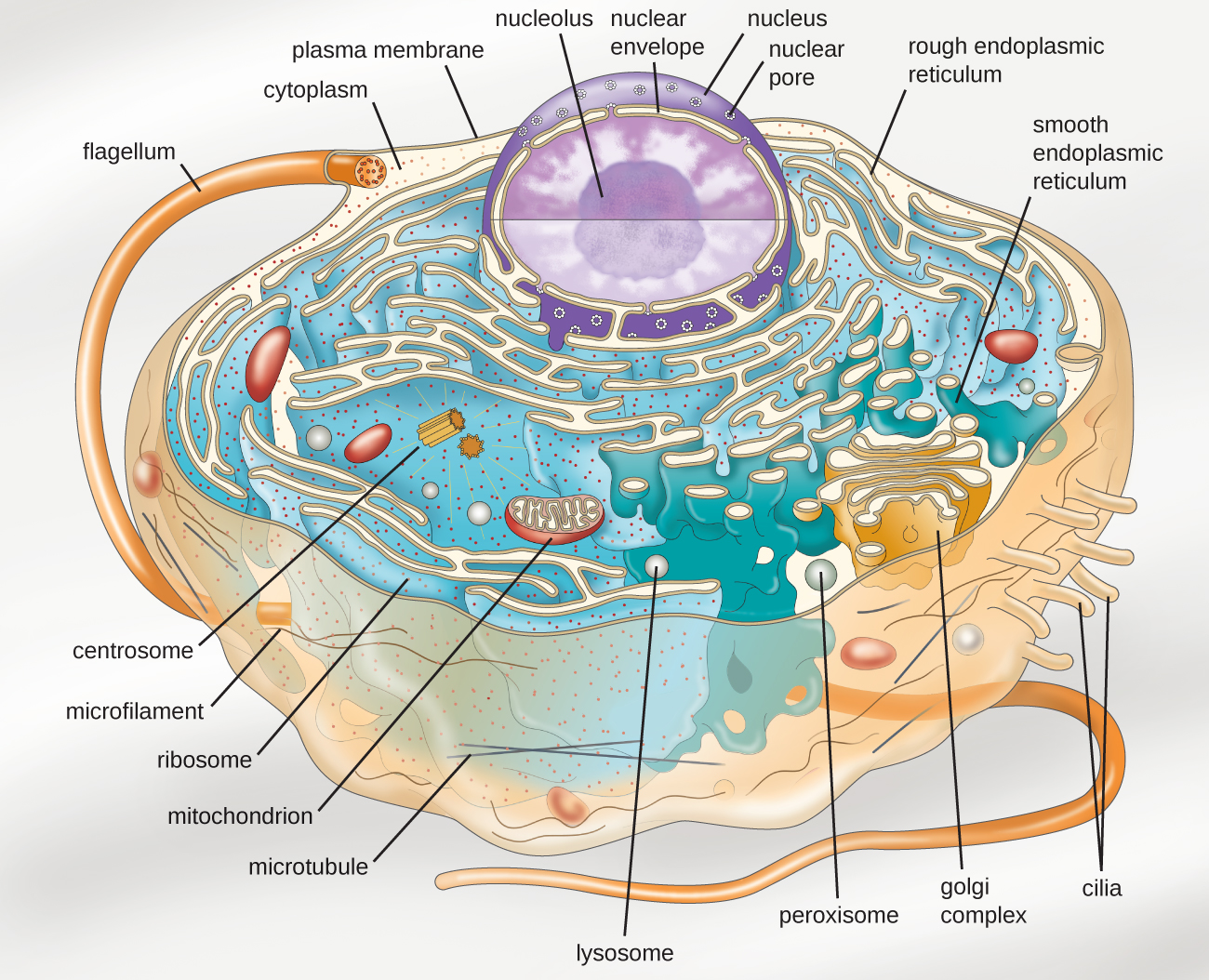
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others.